Unlike conventional T cells that detect peptide antigens loaded to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, unconventional T cells respond to non-peptidic metabolite antigens presented by MHC class I-like proteins, such as CD1 and MHC-related protein 1 (MR1). Semi-invariant mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, γδ T cells, and invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells, together with other CD1- or MR1-restricted T cell subsets expressing diverse T cell receptors (TCR), elicit an innate-like response independent of diverse MHC genetics. In contrast to an overall enhanced response to bacterial-derived riboflavin precursor metabolites in infections, MAIT cells often exhibit an immunosuppressive or exhausted phenotype in glioblastoma, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and various hematological malignancies. Whereas some tumor cells can activate MAIT cells, the structures and functions of tumor-derived MR1 ligands remain largely unknown. Novel discoveries of mammalian-derived agonists and antagonists binding to MR1 protein are our knowledge of MR1 ligand structures and functions from MAIT cell activation in healthy conditions to anti-cancer immunity. Recent findings reveal that nucleoside and nucleobase analogs, as self-metabolites to activate MR1-restricted T cells, are regulated in the tumor microenvironment. Likewise, iNKT cells exhibit a dynamic role in cancer, capable of both protumor and antitumor immunity. Similarly, γδ T cells have also demonstrated both protective and tumor-promoting roles, via recognizing stress-induced protein and metabolite ligands. This review further depicts the distinct kinetics of responses, highlighting a rapid activation of unconventional T cells in solid versus hematological cancers. Emerging therapeutic strategies, including antigen-loaded MR1 and CD1, adoptive T cell transfer, chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T) cells, T cell receptor-T (TCR-T) cells, and combination treatments with immune checkpoint inhibitors, yet remain challenging, hold promise in overcoming tumor-induced immunosuppression and genetic restriction of conventional T cell therapies. By addressing critical gaps, such as novel structures and functions of cancer metabolite antigens, unconventional T cells offer unique advantages in anti-cancer immunotherapy.
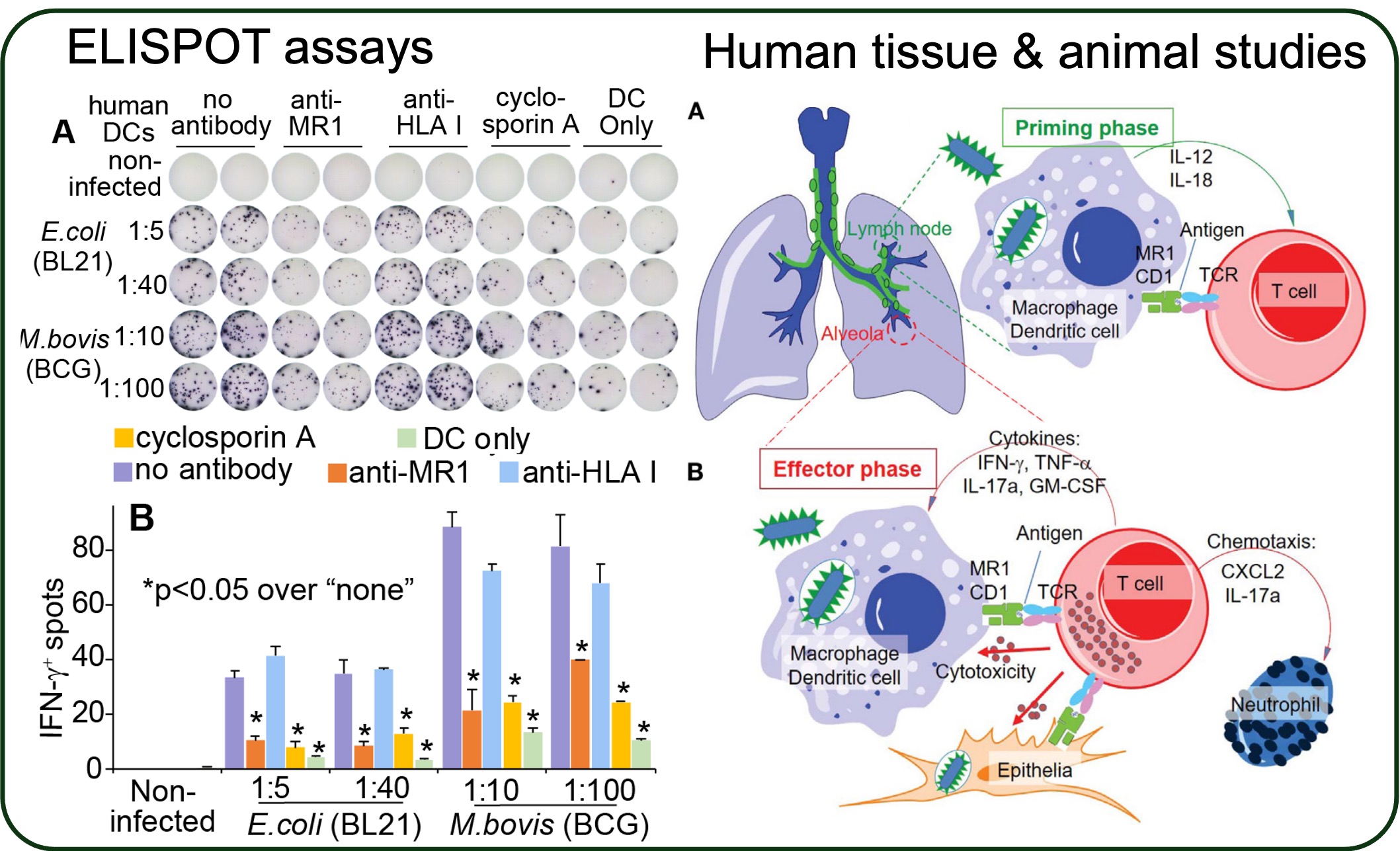 MAIT cell subset is becoming a promising T cell candidate to fight infections and cancers. Animal studies in mice at a loss-of-function of antigen-presentation and gain-of-expression of MAIT TCR supported a protective role of MR1 and MAIT cells in fighting Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. However, its protection in larger animals and humans required to be further tested using optimal strategies for MAIT cell stimulation. We will apply animal models to understand MAIT cell activation and protection in M. tuberculosis infections.
MAIT cell subset is becoming a promising T cell candidate to fight infections and cancers. Animal studies in mice at a loss-of-function of antigen-presentation and gain-of-expression of MAIT TCR supported a protective role of MR1 and MAIT cells in fighting Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. However, its protection in larger animals and humans required to be further tested using optimal strategies for MAIT cell stimulation. We will apply animal models to understand MAIT cell activation and protection in M. tuberculosis infections.